DLR GPS Receiver (Secondary Mission Payload)
There is an MOU between NTU/CREST and DLR to fly on-board XSAT micro-satellite mission a DLR GPS Receiver.
On one hand, the goals for DLR is to conduct experiments onboard XSAT to demonstrate precise real-time navigation using ionosphere-free single-frequency GPS measurement (2m in earth-pointing mode) as well as to show robust navigation across outages (100m on sun-pointing mode). On the other hand, the goal for NTU is to use the DLR GPS Receiver as a redundancy back-up of a GPS for use in ADCS and time synchronization.
The DLR GPS RX is also called XSAT Navigation System (XNS) for the project. The XNS comprises of a Phoenix GPS Receiver with software enhancements for orbit determination and orbit prediction. The XNS hardware comprises a Phoenix GPS receiver with interface board in a common housing as well as an external preamplifier and a passive GPS antenna. The real-time orbit determination software operates inside the Phoenix receiver, which results in a highly-integrated navigation system. (See Fig1.2 below, a picture taken from the XNS ICD documents)
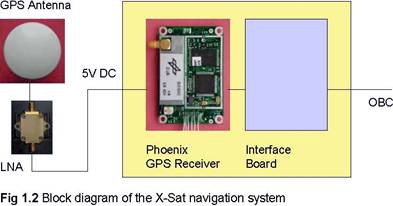
Between the GPS antenna is the LNA (low-noise-amplifier). The antenna for the Phoenix GPS receiver will be mounted with a bracket on the XSAT micro-satellite with its bore sight direction aligned with the –z-axis of the micro-satellite, namely zenith-facing during Earth-pointing mode and Sun-facing during Sun-pointing mode.
The key specifications for antenna are:
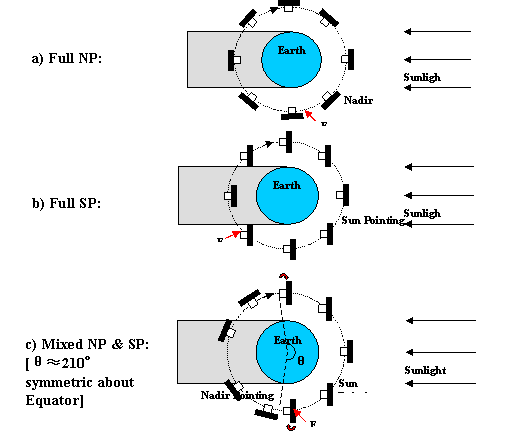
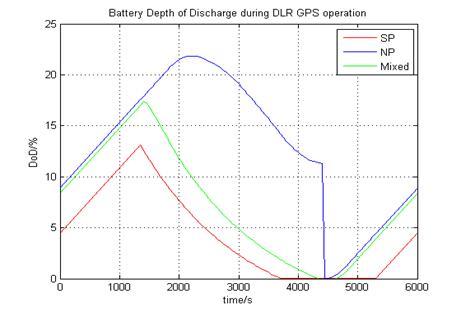
Summary (at April 06) The progress of DLR GPS RX has been good. In harmonizing with XSAT schedule, the schedule for XNS is as follows: Both DLR and NTU has analyzing and discussed together (Dec 05) the operation scenarios for conducting the DLR GPS RX experiment. Preliminary, there is a need to combine sun-pointing mode and earth-pointing mode (rather than 48hour earth-pointing mode) to conduct the experiment in such a way that XSAT’s battery does not go below 20% Depth of Discharge. The following diagram depicts the operation of full nadir-pointing, full sun-pointing and mixed nadir- and sun-pointing.
Weight
55g includes nuts and washer
Diameter
55.9mm
Height
12.2mm
Power handling
1 watt
Temperature
-55° to 85°C
Vibration
10g
Frequency
L1
Polarization
RHCP
The LNA will be designed based on M/A-COM’s AM 50-0002 low noise amplifier chip. No filtering is provided yielding a total bandwidth of about 400 MHz (at 3dB gain loss) with peak amplification at the L1 frequency. DC power for the operation of the amplifier is provided via the receiver connector (labeled “Rx”).
The key specifications for LNA are:
Weight
16g
Size
44.0x33.0x10.5mm (inclu. Connectors and mount)
Height
12.2mm
Power consumption
0.1 watt
Temperature (operating)
-40° to 85°C
Max input power
17dBm
Gain (min/max)
25/29dB
Polarization
RHCP
The key specifications for Receiver are:
Weight
250g (max)
Size
102x86x38mm (includes Ground plane and LNA)
Power consumption
0.1 watt
Temperature (operating)
-20° to 60°C