Using WebView by Example
References: "Building web apps in WebView" @ https://developer.android.com/guide/webapps/webview.
The WebView objects allow you to display web content as part of your activity layout, i.e., it is a simple browser. However, it lack some of the features of full-function browsers.
Example 1: Two Activities
In this example, we shall create two activities (screens) (See "Example: Using an Intent to Start a Second Activity"). The first activity (MainActivity) contains a button to request for a web page. Clicking the button launches the second activity (WebViewActivity) showing the requested web page inside a WebView object.

Step 1: Start a new Project
Start a new Android project with "Empty Views Activity", called "Test WebView".
Step 2a: Define Layout in "res\layout\activity_main.xml"
Replace the existing XML file with the following:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:orientation="vertical" > <Button android:id="@+id/btnGo" android:onClick="btnGoHandler" android:text="GO" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> </LinearLayout>
We use LinearLayout to hold one "GO" button, which triggers "buttonGoHandler" on click.
Step 2b: Program "MainActivity.java"
package ......; import ......; import android.content.Intent; import android.view.View; public class MainActivity extends ...... { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); // use "res/layout/activity_main.xml" } // On-click handler for the "GO" button public void btnGoHandler(View view) { // Create an Intent to start the second activity called "WebViewActivity" Intent intent = new Intent(this, WebViewActivity.class); // Start the intended activity startActivity(intent); } }
The button handler creates an Intent and starts the "WebViewActivity".
Step 3a: Create a Second Activity "WebViewActivity" for an WebView Object
Right-click on "Java" node ⇒ "New" ⇒ "Activity" ⇒ "Empty Views Activity" ⇒ In "Activity Name", enter "WebViewActivity" ⇒ In "Layout Name", enter "activity_web_view" (default) ⇒ In "Package name", enter "com.example.testwebview" (default) ⇒ Finish.
Step 3b: Define Layout in "res\layout\activity_web_view"
This layout (in RelativeLayout) contains one Button (for future use) and one WebView object, as follows:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" > <Button android:id="@+id/btnTodo" android:text="FOR FUTURE USE" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> <WebView android:id="@+id/webView" android:layout_below="@id/btnTodo" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> </RelativeLayout>
Step 3b: Program "WebViewActivity.java"
package ......; import ......; import android.webkit.WebView; public class WebViewActivity extends ...... { private WebView webView; // for displaying web contents @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_web_view); webView = (WebView) findViewById(R.id.webView); //webView.getSettings().setJavaScriptEnabled(true); // 1. URL hardcoded webView.loadUrl("https://www.google.com"); // 2. Start your Tomcat (having the "hello" webapp). // Use the following URL to trigger the HelloServlet with URL "sayhello" on emulator. //webView.loadUrl("http://10.0.2.2:9999/hello/sayhello"); // 10.0.2.2 is the special IP for the host machine of the emulator. // You cannot use localhost, as it refers to the emulator. // 3. For actual phone, use ipconfig (Windows) or ifconfig (macOS) to check your IP address //webView.loadUrl("http://ip_addr:9999/hello/sayhello"); } }
The WebView object invokes loadUrl() to load a hardcoded URL.
Take note that you cannot use localhost (127.0.0.1), which refers to the android emulator. You can use a special IP 10.0.0.2 to refer to the host machine of the emulator, or find out the host's IP address.
Step 4: Modify "AndroidManifest.xml" for Permission
Add the lines in red to the generated manifest.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest ......>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
<application
android:usesCleartextTraffic="true"
.......
......>
<activity android:name=".WebViewActivity"></activity>
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
Notes: android:usesCleartextTraffic="true" is needed to support HTTP; otherwise, only HTTPS is supported.
Step 5: Run the app
Try running the app.
Step 6: Try
Try modify the "FOR FUTURE USE" button as "BACK" button to return to the first activity.
Example 2: One Activity
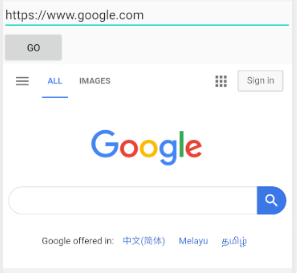
In this example, we have one activity that contains a EditText for entering the URL, a Button to trigger the URL and a WebView to display the web page.
Step 1: Start a new Project
Start a new Android project with "Empty Views Activity", called "Test WebView 2".
Step 2a: Define Layout in "res\layout\activity_main.xml"
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" > <EditText android:id="@+id/txtURL" android:text="https://www.google.com/" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> <Button android:id="@+id/btnGo" android:onClick="btnGoHandler" android:text="GO" android:layout_below="@id/txtURL" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> <WebView android:id="@+id/webView" android:layout_below="@id/btnGo" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> </RelativeLayout>
Step 2b: Program "MainActivity.java"
package ......; import ......; import android.view.View; import android.webkit.WebView; import android.widget.EditText; public class MainActivity extends ...... { private WebView webView; // for displaying web contents private EditText txtURL; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); webView = (WebView) findViewById(R.id.webView); //webView.getSettings().setJavaScriptEnabled(true); txtURL = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.txtURL); } // On-click handler for the "GO" button public void btnGoHandler(View view) { // show the web page of the URL of the EditText webView.loadUrl(txtURL.getText().toString()); } }
Step 3: Modify "AndroidManifest.xml" for Permission
Add the lines in red to the generated manifest.
<?xml ......?>
<manifest ......>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
<application
android:usesCleartextTraffic="true"
......
......>
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
Notes: android:usesCleartextTraffic="true" is needed to support HTTP; otherwise, only HTTPS is supported.
Step 4: Run the App
Try these URLs (https and http):
- https://www.google.com
- Start your Tomcat server (having "hello" webapp and
HelloServlet) and issue http://10.0.2.2:9999/hello/sayhello (10.0.2.2 is a special IP for the host machine of the emulator). - On actual phone, find out your IP address (via command
ipconfig(windows) orifconfig(macOS)) and issue http://ip_addr:9999/hello/sayhello