Introduction
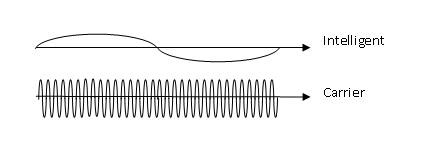
In telecommunication, the term modulation is a process that varies a modulating signal (intelligent) on to a higher frequency signal (carrier).
Waveform Comparison

Reasons for Modulation
Types of Modulation
There two general types of modulation namely analogue and digital. Different parameters are been varied to achieve different resultant waveforms.
Analogue
There are 3 major classes of Analogue modulation techniques used for Analogue transmission. They are namely:
AM works by varying the amplitude of the transmitted signal before Transmission. Transmitted waveforms produced are
FM works by varying linearly of the instantaneous carrier’s frequency with the intelligent signal before transmission.
PM works by varying linearly of the instantaneous carrier’s phase by 0° or 180![]() with the intelligent signal before transmission.
with the intelligent signal before transmission.
Analogue - AM
DSB uses full power transmission contributed by both sidebands and carrier. When the signal is generated, three spikes will appear in the spectrum domain. They are namely
DSB-SC suppresses the carrier of the waveforms which helps reduced transmission power, as the carrier (Fc) does not carry any information. This reduction will:
SSBfurther reduces one of its sidebands (LSB) and ultimately contribute to even more efficiency usage of both the electrical power and bandwidth (BW).
Digital
There are 3 major classes of digital modulation techniques used for digital transmission. They are namely:
ASK is a form of modulation that represents digital data as variations in the amplitude of a carrier wave.
FSK is a frequency modulation scheme in which digital information is transmitted through discrete frequency changes of a carrier wave.
PSK is a digital modulation scheme that conveys data by changing, or modulating, the phase of a reference signal (the carrier wave).
Filters
Filters act like a frequency-selective components which are commonly found in communication circuits. By passing or attenuating different frequencies, different types of filters can be achieved. There are 4 general examples of filter namely;