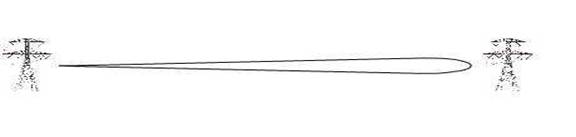
High frequency beamwidth
Millimeter Wave
Millimeter Wave (also known as MMWave) can loosely be defined as electromagnetic waves with frequency range from 30 GHz to 300 GHz. It covers the highest band of Radio Frequency Bands, namely Extremely High Frequency (EHF) band.
Applications
The applications of millimeter wave can be classified to four categories: - communication, sensor, studies and experiments, and weapons systems.
A. Communication
Millimeter wave is used in many communication systems especially terrestrial and satellite communication, and wireless data transmission. Its data rate may reach 40 to 100 times higher than that of wireless LAN.
B. Sensor
Because of its ability to operate well in any weather conditions, millimeter wave technology is used in Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS). Some of the applications are: automotive radar, and radar for infrastructure. There are other applications of millimeter wave sensors as well, for example: autonomous cruise control, speed and range sensors for industrial usages, aircraft anti-collision sensor, robotic vision, imaging, motion sensors, safety and security sensors and many more.
C. Studies and Experiments
In some studies and experiments, millimeter wave is useful to produce more precise measurements in magnetic resonance with very high frequency and Fourier transform systems. This is because it may able to improve the resolution of spectral and sensitivity of experiments.
D. Weapons Systems
Active Denial System (ADS), U.S. Air Force weapons systems is used to emit millimeter wave with wavelength of 3 mm. Millimeter wave radar subsystems are applied in many other military usages as well, some of them are missile guidance, navigation guidance, surveillance systems for Air Defense, and location tracking for Snipers.
The Need to use of Millimeter Wave In Future and Advantages
Nowadays, microwave is more and more commonly used in many applications. Therefore, the frequency bands of microwave may be fully used in the future. Hence, millimeter wave can be used as a solution. Furthermore, using millimeter waves have following advantages.

High frequency beamwidth
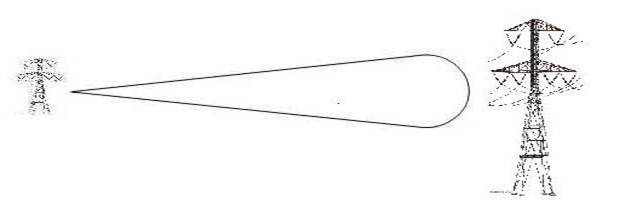
Low frequency beamwidth
Figure1. at lower frequencies, the beam width is wider, hence bigger antenna is needed
Disadvantages of Millimeter Wave
Compared with microwave, using of millimeter wave also has some disadvantages.
Usage of Millimeter Wave technology in Singapore
According to IDA (Infocomm Development Authority of Singapore) the frequency bands above 30GHz are currently not occupied. Millimeter wave technology has the advantage over the rainy climate in Singapore since millimeter waves are not easily prone to interference. The researchers are encouraged to explore this technology. IDA will make these frequency bands available once there is demand for them. For further information, please visit www.ida.gov.sg .
References List
Future improvements