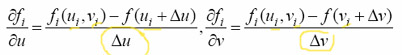Last time updated: 29/10/2005 08:49
page vii: ...“off-the-shelf”
page viii: ...explained in Chapter
4, while Chapters 5
and 6 deal with three-dimensional geometric and
projection transformations.
page ix: ...who has borne
a heavy burden
page 12:
pallettes
page 19:
x2
= 240000
page 20: address( x, y ) = 1000*y + x
address(400,500) =
1000*500 + 400 = 500,400.
page 25: Ellipse:

page 26: Straight
line: y-y2
page 32: Sphere
Explicitly
![]()
Ellipsoid
Implicitly:
![]()
page 36: Figure 3.15: Upper P2 is to be R2
page 39:
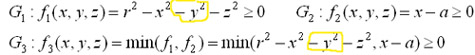
page 41: x(t,u) = 4t + 12u
page 44: Suppose that the.... to the coordinate plane XY..."
page 45: representation of a segment
page 49: By setting a and d to any…
page 50:
A
Shear proportional to the x coordinate
(Figure 4.4)
while b≠0 yields a shear proportional to the y coordinate
(Figure 4.4).
page 51: Figure 4.4 Shear proportional to Y coordinate.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
![]()
page 57: Also, the associative law T1(T2T3)=(T1T2)T3 applies.
…listed backward in contrast…
page 57:

page 60:

page 61: c) 1010 & 0010 = 0010 rejected
page 63,64: x', y'
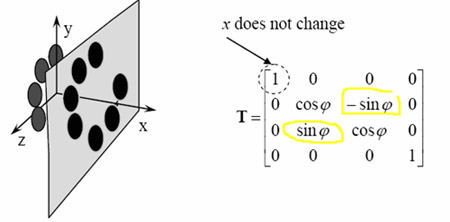
page 70: about axis Z only x and y coordinates change.

page 74:
page 77: 
page 84: 6. b
page 92:
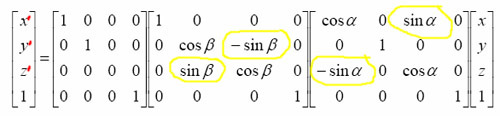
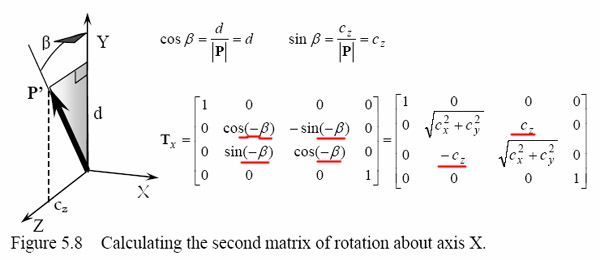
page 93: vector PP’=ku=[ kcosθcosf kcosθsinf -ksinθ ]. The following will also hold for point P’:
page 98: (Figure
6.16)
page 100:
page 103: Figure 6.21: point (1,0,0)
For any point P and its projection P’ we can write PP’=kv=[0.7k 0 -0.7k],
..................................................................................x'=x+z

page 104: on axis Z.
page 108:
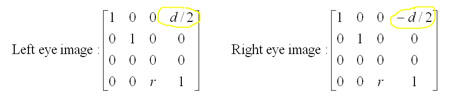
Q5 (b) ... orthographics
parallel
(c) ... consider the remaining two as the 2D
coordinates of the ...
page 110:

page 113:

page 116: For colour light
page 117-130:
Gouraud
page 126:
... and angle
g
between the reflected ray and the vector to the
observer is 0°.
Therefore:
I=Ka×Ia+Kd×Id×cos(a)+Ks×Is×cosn(g)
page 133: P(t)=P1(1-t)+P2t
0ŁtŁ1
page 135:
P(t)=(1-
t)2P1+2t(1-
t)P2+
t 2P3
P(t)=(1- t)3P1+3t(1-
t)2P2+3t
2(1- t)P3+t3P4
page 145: (r-hp)
(hp-r)
page 162: ...In contrast
page 151:
![]()
page 153: The required transformation is illustrated in Figure Q4.
page 159:

page 160:

page 250: